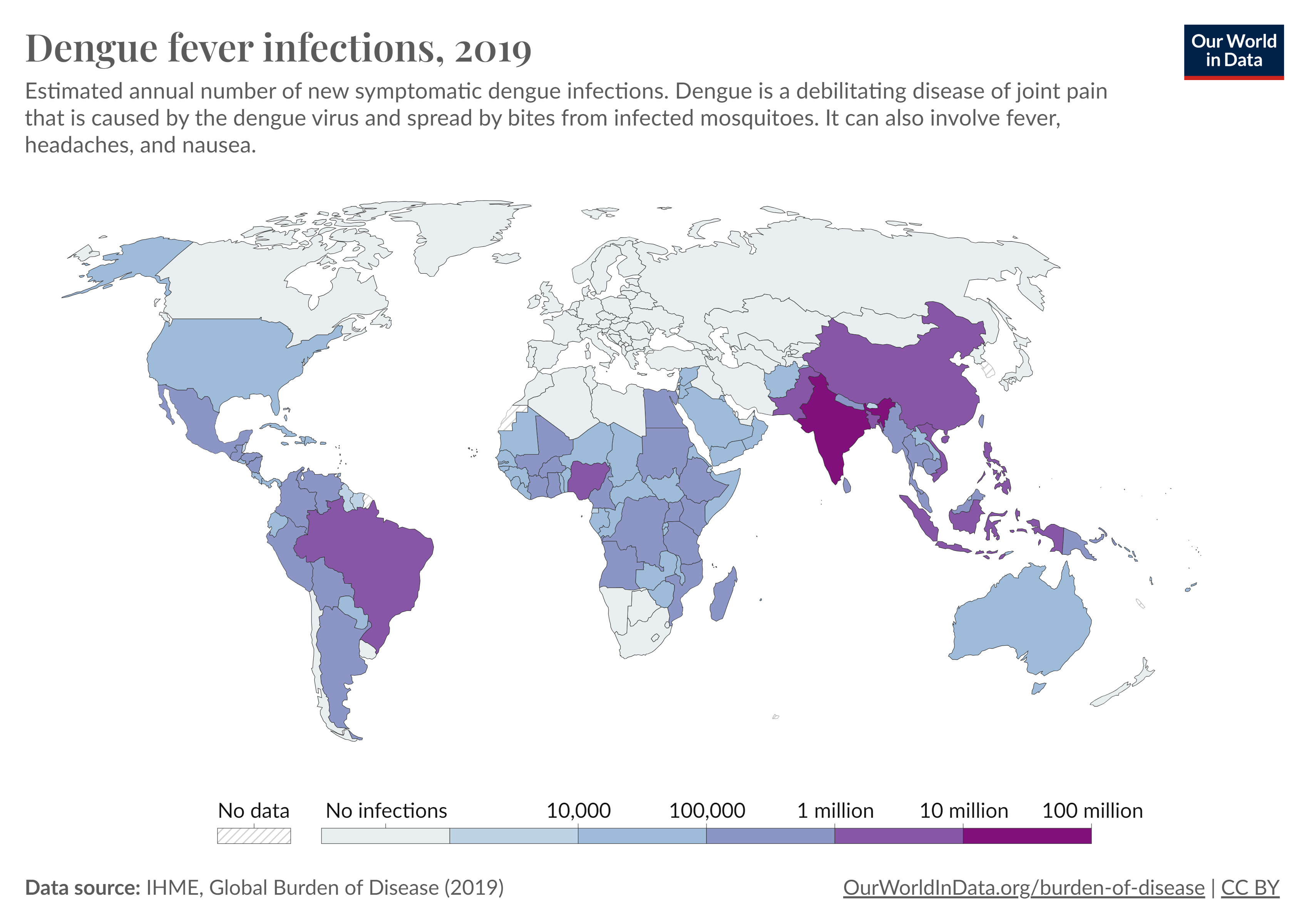
6 Dengue
Dengue is a viral infection that spreads to people through the bite of an infected Aedes species (Aedes aegypti or Aedes albopictus) mosquito. About half of the global population is currently at risk of contracting dengue fever, with an estimated 100 to 400 million infections occurring annually. Dengue is prevalent in tropical and subtropical regions worldwide, primarily in urban and semi-urban areas.
Although many infections of the dengue virus (DENV) do not show symptoms or only result in mild flu-like illness, some cases can be severe and potentially fatal. Dengue fever does not have a specific treatment. Early detection and timely access to proper medical care significantly reduce the fatality rates associated with severe cases. Preventing and controlling dengue transmission relies on managing the the mosquitoes that act as vectors.

